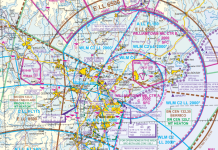
- Overhead Bundaberg (YBUD), climbing into Class E airspace, what frequency should be contacted for clearance?
- BN CEN 124.1
- BN CEN 121.2
- Bundaberg 124.1
- BN CEN 135.2
- The asterisk (*) at Gladstone next to the VOR denotes:
- the navaid is pilot monitored
- an NDB is co-located with the VOR and the frequency is not shown
- an ILS and DME are at Gladstone
- the navaid is subject to operating limitations
- 185 knots
- 240 knots
- What is an IFR pick-up?
- upgrading the flight from VFR to IFR due to weather
- a flight operating under the IFR in Class G airspace changes to VFR when entering Class E airspace while awaiting an airways clearance
- a flight operating under the VFR in Class G airspace changes to IFR when entering Class E airspace
- a clearance relayed through another aircraft when contact cannot be made with ATC due to VHF limitations
- Airway W636 for navigation between YBUD and YGLA is available for:
- tracking to the north only
- tracking to the south only
- tracking in both directions at all levels
- tracking in both directions OCTA only
- Overhead Gladstone (YGLA) at 8,000 feet, what class of airspace are you in?
- Class C
- Class D
- Class E
- Class G
- The brown shaded background in the airspace around Bundaberg represents:
- CLASS G airspace
- CLASS E airspace with a lower limit above 10 000 feet AMSL
- CLASS E airspace with a lower limit below FL125
- Military CTA that overlays CLASS G airspace
- In airspace where ATC approval is not required to change level, ATC reporting requirements for an IFR flight when making a level change, are:
- no reports required
- present position must be reported approximately one minute prior to making the change
- present position and intention must be reported approximately one minute prior to making any change
- present position and intention must be reported within 2 minutes of making any change
- Airways designated on the chart with an identifier V or W are:
- available for use in non-controlled airspace only
- available for use in controlled airspace only
- area navigation routes
- not area navigation routes
- Airway Z84 to Bundaberg is:
- an area navigation route
- not an area navigation route
- available in Class E airspace only
- available for operations OCTA only
- Area navigation allows operations on:
- any aircraft flight path within the coverage of ground-based navigation aids only
- any aircraft flight path within the coverage of ground-based navigation aids, space-based navigation aids or self-contained navigation aids, or any combination of them
- any aircraft flight path flown within controlled airspace only
- an aircraft flight path for published terminal arrival (STAR) and departure (SID) procedures only
- The LSALT specified for a route segment is only valid for which operations?
- RNP2
- RNP10
- for operations within the rated coverage of the navaids being used
- area navigation operations
- To operate to RNP2 standards, a Part 91 IFR operation must comply with which of the following?
- a specific operator approval is required
- if approved to do so in the aircraft flight manual
- if the PIC is authorised to conduct RNP AR operations
- RNP2 operations are only permitted for Part 135 and 121 operators
- To use an electronic flight bag (EFB) for enroute charts, what limitations apply?
- only for use during enroute operations, and not available for instrument approaches
- allowed only for VFR operations unless the PIC is endorsed to use EFB information
- paper charts are required in controlled airspace unless a backup device is carried
- provided the information comes from an approved data provider
- Current approved data providers for EFB information include:
- Jeppesen, Avsoft, Garmin, Ozrunways and Foreflight
- Airservices Australia only
- any EFB data can be used and, if it has a moving map and valid GPS, it can be used for navigational purposes
- FAA-provided information is the only data approved for EFB use in Australia
- One limitation of ERC Low charts is?
- they are only valid up to 8,500 feet
- they are only valid up to FL110
- they are designed primarily for aircraft operating transcontinental and intercity capital routes.
- aeronautical information within terminal areas may not be complete and pilots should use a TAC or VTC
To view the answers, go to the next page using the page navigation buttons below.





Comments are closed.