A Category B aeroplane is required to circle for runway 18 in Cooma via the following approach:
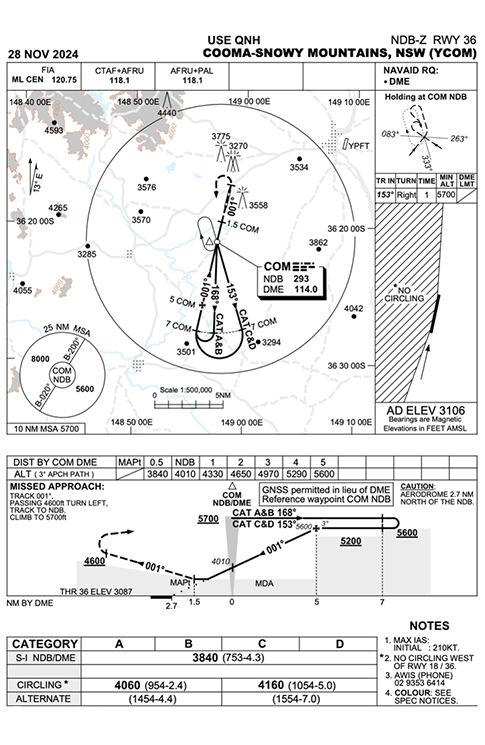
- What is the maximum CAT B speed for circling?
- 140 knots IAS
- 135 knots IAS
- 130 knots ground speed
- 140 knots TAS
- What is the minimum obstacle clearance required above the highest obstacle within the circling area (Cat B)?
- clear of obstacle
- 200 ft
- 300 ft
- 400 ft
- What is the CAT B circling radii (reference only) for this procedure?
- 2.66 nm
- 2.71 nm
- 2.77 nm
- 2.63 nm
- What is the recommended timing FROM passing abeam the threshold of runway 18, TO commencing the base turn onto runway 18 (before correcting for tailwind)?
- 30 secs
- 20 secs
- 40 secs
- 25 secs
- Spot heights on instrument approach and landing (IAL) charts encompass all potential obstacles including the highest points in the relevant circling area. True or False?
- true
- false
- If the DME is NOTAMed as being out of service, can GNSS be used in lieu of the DME?
- yes
- no
- Descent below the minima of 4,060 feet (with the required visual references) should not be made until:
- the minimum visibility can be maintained
- the aeroplane can maintain a minimum height of 300 ft AGL
- the aircraft is in a position to carry out a landing using normal rates of descent and angles of bank
- the aeroplane can maintain a minimum height of 500 ft above aerodrome level (AAL)
- What minimum clearance do the 25 nm MSA and the 10 nm MSA provide above all objects?
- 2,000 ft within 25 nm, 1,000 ft within 10 nm
- 2,000 ft
- 1,000 ft within 25 nm of the NDB, and 1,000 ft within 10 nm of the aerodrome reference point
- 1,000 ft
- Threats presented by this circling approach may include (but are not limited to) which of the following:
- higher elevation resulting in increased TAS and groundspeed
- higher radius of turn for a given angle of bank due to field elevation
- increased rate of descent to fly a three-degree landing profile due to field elevation
- all of the above
- What methods may be used to mitigate the threats?
- flying an IAS less than the maximum allowed if possible and taking landing configuration early
- increasing the available circling area by operating as a higher category aeroplane
- circling to the west of the runway if this means you have a headwind on base
- all of the above
- On the graphical area forecast (GAF) excerpt shown, what does the term ISOL mean?
- +TSRA forecast to occur as a single cell only
- +TSRA forecast to affect up to 50% of an area
- +TSRA to affect 100% of the area with less than 30 minutes duration
- 500 m visibility in isolated areas
- What does the term EMBD in the GAF mean?
- embedded within cloud layers and cannot be readily recognised
- little or no separation between adjacent features affecting greater than 75% of an area
- cumulus cloud combined with other forms of cloud
- only applies to isolated cumulus formations in overwater areas
- An AIRMET contains observed or forecast information (for deteriorating conditions only) when not forecast in the relevant GAF. Which of the following deteriorating conditions would be provided in an AIRMET?
- changes in the freezing level specified in a GAF of more than 1,000 feet
- any surface visibility below 10 km not specified in a GAF
- light icing
- towering cumulus
To view the answers, go to the next page using the page navigation buttons below.