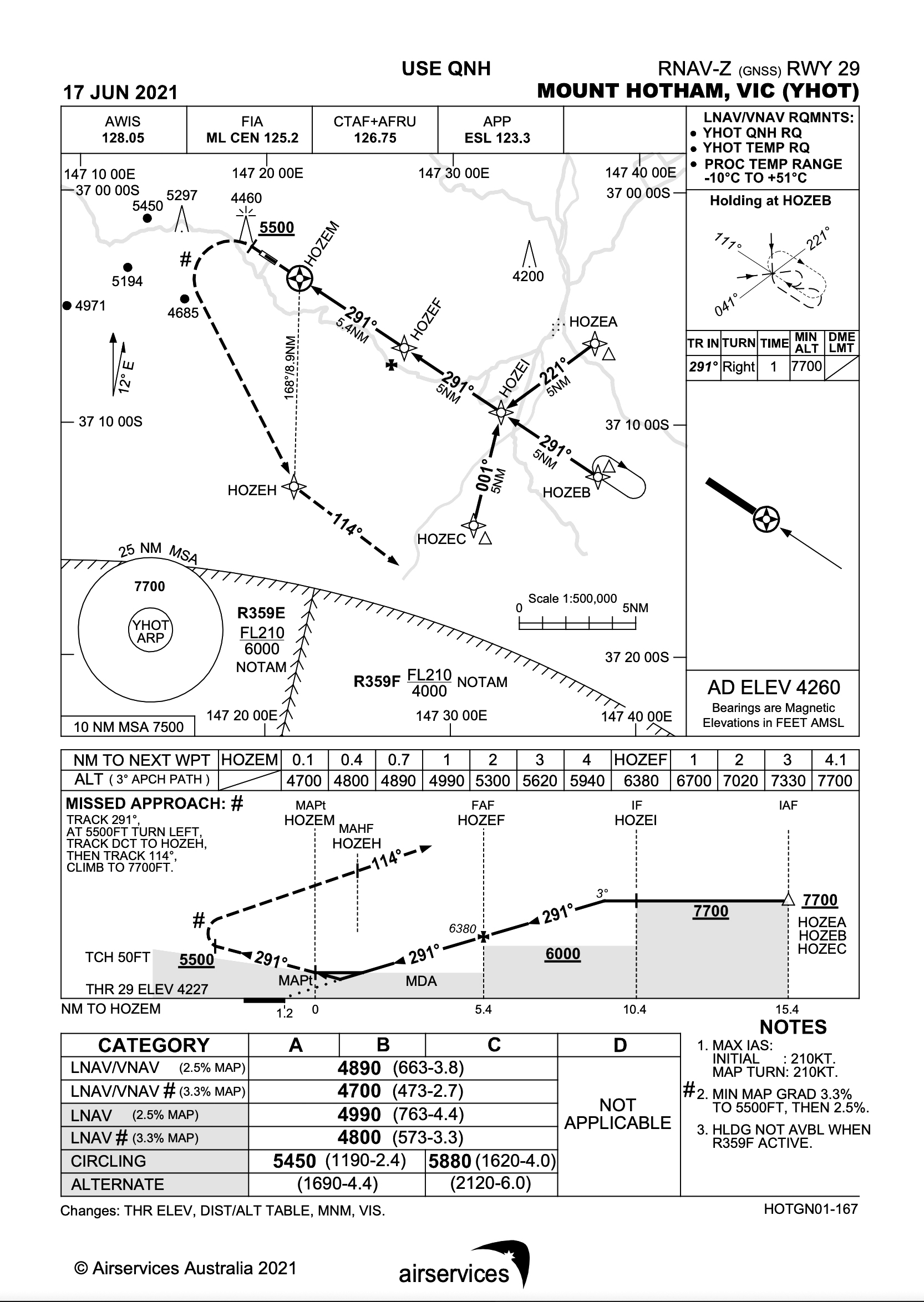
Sally wants to fly into Mount Hotham Airport (YHOT), elevation 4,260 feet, with her friends for a day of skiing. YHOT is an aerodrome that requires prior permission from the operator to use (refer ERSA).
Sally has approval to conduct a research flight, involving an approach to the minima and missed approach without landing, on the type of winter’s day she would be seeking to go there. She has also conducted this approach in summer.
She has studied all the provided material and is planning an early morning approach on a cold winter morning, just after a day of heavy snowfall. Skies are mostly clear except for patches of low cloud and mist. The AWIS temperature for her arrival is minus 10 °C.
Sally is operating a twin-engine aircraft that has no temperature compensation capabilities, with a GNSS capable of displaying an advisory vertical profile (the vertical component is generated by the receiver itself). The aircraft is not capable or certified to operate to the LNAV/VNAV minima, only the LNAV minima.
1. When Sally conducted the same approach in summer, on a hot (ISA+25 day), she was high on the PAPI when becoming visual, after accurately flying a constant descent approach in accordance with all the procedure altitudes. In warmer than ISA conditions, an altimeter system flying a published barometric based approach will:
- Under read, meaning the aircraft’s true altitude is lower than indicated. The gross flight path error increases as altitude lowers towards the minima.
- Over read, meaning the aircraft is higher than indicated. The gross flight path error does not change with altitude.
- Over read, meaning the aircraft is higher than indicated. The gross flight path error decreases as altitude lowers towards the minima.
- Under read, meaning the aircraft’s true altitude is lower than indicated. The gross flight path error does not change with altitude.
2. In colder than ISA conditions, an uncompensated basic pressure altimeter system:
- Over reads, meaning the aircraft is lower than indicated. The gross error increases with altitude.
- Under reads, meaning the aircraft is higher than indicated.
- Under reads, and the gross error decreases with increasing altitude.
- Over reads, meaning the aircraft is higher than indicated.
3. Below what airport temperature should cold weather temperature altitude corrections be applied at YHOT for an approach to the LNAV minima?
- 0 °C
- –5 °C
- –8 °C
- –10 °C
4. The altitudes that require a correction for non-standard temperatures are:
- DA only
- MDA only
- DA and MDA only
- DA, MDA and all procedure altitudes
5. With –10 °C reported via AWIS, the minimum altitude prior to the Intermediate fix HOZEI is 7,700 feet. What indicated altitude is required to be flown to ensure a true altitude of 7,700 feet when conducting the LNAV approach?
- 7,700
- 7,480
- 7,920
- 8,470
6. Approaching the aerodrome, Sally is above the MSA and LSALT, and on an inbound track of 201 to HOZEB. Her GNSS shows a track of 245 required to HOZEA. Based on these tracks, to conduct the approach without entering the holding pattern, Sally can commence the approach from:
- her current track to HOZEB or tracking direct to HOZEA
- her current track to HOZEB only
- a direct track to HOZEA only
- HOZEB, HOZEA or the IF, HOZEI
7. At position HOZEF, it is clear that mist and cloud will prevent further descent to the minima without entering cloud and resultant exposure to icing conditions. Sally elects to commence the missed approach from 5,300 feet indicated altitude between HOZEF and the minima. The correct actions for the missed approach are:
- Commence an immediate left turn and track direct to HOZEH
- Continue to track towards HOZEM, do not turn left until after HOZEM and passing 5,580 feet indicated altitude
- Fly a level segment until the missed approach point HOZEM, then turn left and track direct to HOZEH
- Once above 5,500 feet, turn left and track direct to HOZEH
8. The LNAV/VNAV minima differ from the LNAV-only minima in which way, with regards to Decision Altitude (DA) and Minimum Descent Altitude (MDA)?
- The LNAV/VNAV minima is a DA and the LNAV minima is an MDA.
- Both the LNAV/VNAV and LNAV minima are MDA.
- Both the LNAV/VNAV and LNAV minima are DA if actual QNH is used.
- The LNAV minima is a DA if actual QNH is used.
Answers
- (c)
- (a)
- (c)
- (d)
- (c)
- (c)
- (b)
- (a)






Some references would be nice
Some references in the AIP are found in the ENR 1.5 section, while DAP 2.2 and 2.3 have the cold temperature correction tables.