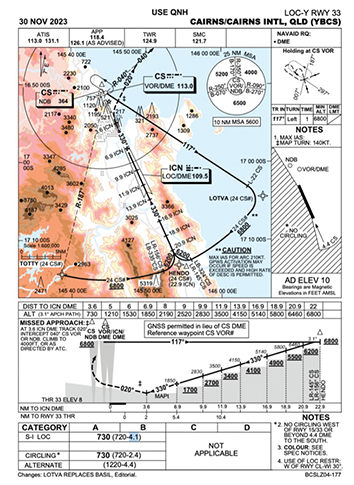
- What is the segment minimum safe altitude or ‘not below’ altitude at 13.9 DME?
- 4,100 feet
- 4,150 feet
- What is the 24 DME ARC flown with reference to?
- CS VOR/DME
- ICN DME
- What are the tracking tolerances for a DME arc?
- ± 1 nm
- ± 2 nm
- ± 3 nm
- ± 4 nm
- Where is the IAF when joining to fly the reversal procedure?
- established inbound 330 at 24 DME CS
- established on the 24 DME arc
- passing the CS NDB or CS VOR tracking 117 outbound
- Where must the DME arc be joined?
- at or before an IAF
- only after crossing an IAF
- outside 10 nm from the station
- within 2 nm of a published fix
- For what optimal descent profile does the DME distance/altitude scale provide guidance?
- 3 degrees to the runway threshold
- 3 degrees to a point 450 m past the runway threshold
- 3.1 degrees to the runway threshold
- 3.1 degrees to a point nominally 300 m past the threshold
- Published visibility on IAL charts with a straight-in minima generally specifies a distance, measured in km, from the aircraft’s position at the MDA or DA on the published vertical path, to a point located:
- 800 m prior to the threshold
- the runway threshold
- 160 m (500 feet) past the approach threshold, or approach landing lights if appropriate
- the midpoint of the runway
- When tracking via the 24 nm arc, when can you descend below 6,800 feet?
- crossing the LR-145 or LR-156, you can descend to 5,500 feet
- crossing the LR-145 or LR-156, you can descend to 6,200 feet
- within half scale deflection of the LLZ, you can descend to 5,500 feet
- only after passing HENDO, can you descend to 6,200 feet
- What is the maximum speed for crossing 6.9 DME ICN in a category B aircraft?
- 120 knots IAS
- 120 knots groundspeed
- 130 knots groundspeed
- 130 knots IAS
- What is the minimum altitude that can be flown to, before needing to be visual in a Category B aircraft for this approach?
- 630 feet decision altitude (DA)
- 730 feet minimum descent altitude (MDA)
- 630 feet minimum descent altitude (MDA)
- 730 feet decision altitude (DA)
- What is the maximum IAS that can be flown in a Category A aircraft during the missed approach turn?
- 100 knots
- 110 knots
- 140 knots
- 150 knots
- What is the maximum IAS that can be flown in a Category B aircraft during the missed approach turn?
- 110 knots
- 130 knots
- 140 knots
- 150 knots
- What is the maximum IAS that can be flown in the published holding pattern if at or below FL140 prior to commencing an approach?
- 170 knots
- 200 knots
- 230 knots
- 240 knots
- Does a METAR QNH satisfy the requirement of an actual QNH if reported within the last 15 minutes?
- yes
- no
- When becoming visual in rain, the presence of a light film of water on the windscreen can create a visual illusion; how can this make the approach look to the pilot?
- steeper than it actually is which can feel high on the approach
- shallower than it actually is which can feel low on the approach
- further to the runway than it actually is
- no illusion will be experienced
To view the answers, go to the next page using the page navigation buttons below.





